Crawford’s Auto Repair provides electrical system services, including starter system repair, ignition system repair, charging system repair and alternator repair for customers from Chandler, Gilbert and nearby areas.
Schedule An AppointmentIf your battery isn't holding a charge, it's difficult to get your engine started, your check engine light is on, or your engine is misfiring, then bring your vehicle to Crawford's Auto Repair. Call 480-201-0740 to schedule an appointment.
When technicians and auto professionals discuss the Electrical System, it refers to a very specific system which regulates the firing order of the cylinders of internal combustion engines. The starter system and the ignition system are both part of the electrical system. Of course the electrical system also includes the battery and alternator (or generator in older vehicles), which is also called the recharging system.
The starter system includes the ignition switch where you turn your key to start the vehicle, safety switch, solenoid, starter motor and the wiring connecting them. The starter system is responsible for turning the crankshaft of the engine, which manually moves the pistons up and down and draws an air-fuel mixture into the combustion chambers. This allows the mixture to be there so that the ignition system can ignite the fuel and start the internal combustion cycle. The internal combustion cycle is also known as the Otto cycle in regular gasoline engines and the diesel cycle in diesel engines. See an alternative description of the electrical system in Lesson 5 of our Beginner’s Guide To Auto Repair & Maintenance online, or download our free ebook.
Thank goodness for modern vehicles which include a starter system so that we can start the engine from the driver’s seat, instead of having to be in front of the vehicle and winding the crankshaft by hand! This is something you might have seen in movies with older vehicles. (Dick Van Dyke’s character having to do it in Chitty, Chitty, Bang, Bang is one example). It’s also the same reason there is a pull cord to start a lawn mower.
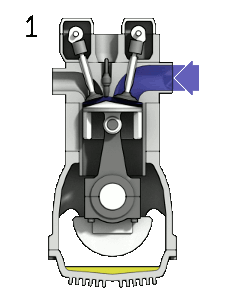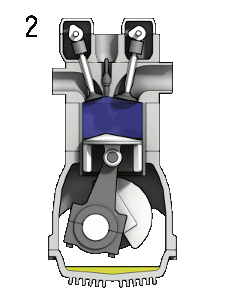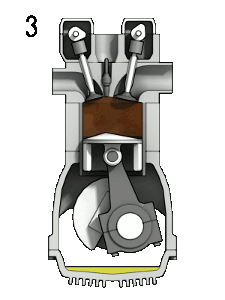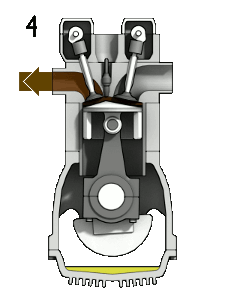
Diagram showing the operation of a 4-stroke spark ignition engine. Labels: 1 ‐ Induction, 2 ‐ Compression, 3 ‐ Power, 4 ‐ Exhaust. CC-BY-SA 3.0 Zephyris
The ignition system is responsible for igniting the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chambers. In regular gasoline vehicles this is done with a spark. If an engine has 8 cylinders then it will have 8 spark plugs which fire in a specific order so that the pistons alternate moving up and down in a continuous cycle. Where the starter motor was initially responsible for turning the crankshaft to which all the pistons are connected in alternating order, it is now the internal combustion process that is causing the pistons to move up and down and turn the crankshaft. The kinetic energy of the turning crankshaft is then transferred to the drivetrain, starting with the transmission, to move the vehicle forward. Learn more about the drivetrain and transmission services.
In a modern vehicle the ignition system consists of a crankshaft position sensor, which sends a signal to the PCM (powertrain control module or computer). The PCM interprets the signal and sends a signal to the ignition coils on each cylinder. Then the ignition coils fire through the spark plugs to create the spark that ignites the fuel. Older vehicles prior to 1975 have different parts to the ignition system which is described in more detail in the Beginner’s Guide. Some of these parts might be included in the list of repairs below.
The fuel system works in conjunction with the ignition system since the fuel has to be injected into the combustion chambers in harmonious order with the firing of the spark plugs. Learn more about Fuel System Services.
The charging system or recharging system consists of a battery and alternator. A vehicle battery provides all electrical power to the vehicle, and it is designed to be frequently discharged and recharged. The value of the battery depends on how many times it can be recharged. Since it takes a lot of power just to use the starter motor, among other electrical parts and accessories, the electrical system also includes an alternator which uses power from the running engine to recharge the battery.
“Ignition” disambiguation: People often refer to the ignition switch or key ignition switch as just “the ignition”. But you’ll also notice that it’s not listed as part of the ignition system above, it’s part of the starter system. Technically “the ignition” is the spark that initiates the internal combustion, not the switch where you turn the key.
What about parts like power locks and windows? Those use electricity, so are they part of the “electrical system”? Once again “the electrical system” refers to the system that is involved in starting and regulating the engine. For further clarification this can also be referred to as the “engine electrical system”, which is distinct from the Chassis electrical system. Learn more about that on our page about Electric Components.
Electrical System Maintenance
Standard maintenance checks are performed at every oil change (about every 5,000 miles) and at landmark mileage including 30,000, 90,000 and 150,000 miles. During these checks the technician will test drive the vehicle and visually inspect the electrical system.
During the test drive the technician will be able see any illuminated dashboard lights and note any signs while starting and driving the vehicle. Many of these signs are listed below.
The parts which are visually inspected include the battery, alternator, alternator belt, wiring and other parts that can be visualized without disassembly. The alternator belt is a part that can be subject to drying and cracking due to overuse and the hot, dry weather we experience here in Arizona.
The battery is inspected for corrosion around the terminals and cables. Any sign of corrosion means there is an issue that needs to be addressed. The battery fluid level is checked if accessible and we perform a battery test. Learn more about battery services.
Ignition System Maintenance – Engine Tune-Up
Beyond standard maintenance with every oil change, your vehicle may also need a tune up at the mileage specified by your vehicle’s manufacturer. A tune-up is traditionally considered to be a spark plug replacement service, but it can also be considered an “internal combustion cycle optimization and timing service”, which includes more than just changing the spark plugs. The vehicle owner’s manual is consulted for the exact mileage when this should be performed; it’s often around 100,000 miles. Learn more about the Engine Tune Up.
Electrical System Dashboard Warning Lights
The following warning lights indicate that your vehicle needs service and it may have something to do with the electrical system. Your vehicle may have a variation of the lights pictured below. Consult your owners manual for the exact lights in your vehicle.
Charging System Light
This is one of the lights that should be memorized so you immediately know what to do when it illuminates. This light could become an emergency real soon, the engine could stop on it’s own at any time. If it comes one while driving then turn off all electronic accessories (AC, heater, unnecessary lights, radio, disconnect phone chargers, etc.) and pull over safely. It’s even more of an emergency at night when you could loose headlights. The temperature light may also come on at the same time.
This light indicates that your battery is not getting recharged after the engine is turned on and running. There is either a problem with the battery itself or there is a problem with the alternator.
Check Engine Light
If this light is illuminated then your vehicle will not pass an emissions test. It could be anything related to the engine, the ignition system or the exhaust system. Learn more about the Check Engine Light Diagnostic.
Starting System Fault Lights
There is something wrong with the starter system. Your engine may not start or it may not start again if you turn it off. Consult the owner’s manual without turning it off and/or drive it directly to the shop.
Engine Fault Indicator-Spanner Service Indicator
This is less common but it indicates there is something wrong with the engine or transmission electronics.
Master Warning Light
This is a general warning light and it is usually accompanied by another more specific light.
Info Light/Check Owner’s Manual Light
These lights indicate that there is a message for you on the control panel or you need to check your owner’s manual for something. This can range in severity. It might be urgent or it might be time for routine maintenance.
Signs Of A Failing Electrical System Which Merit Inspection & Repair
One of the most common signs of a failing electrical system is that the engine won’t start. Either you’ll hear clicking and the engine won’t start or you’ll hear nothing at all. External or internal lighting may dim or electrical accessories may not work at all. This could mean a failed battery, or a failing alternator which is not recharging the battery while the engine is running. It could also mean a fuse has blown that is related to the starter circuit.
If the Charging System Warning light comes on or if the headlights dim while idling then the alternator is failing.
Sometimes the alternator belt is shared between the alternator, air conditioning compressor and water pump. In these cases it is called the serpentine belt or the drive belt, and if this belt is damaged or loose then there will also be signs related to the air conditioning and cooling systems (since the water pump is part of the cooling system). The Serpentine Belt is not the same as the Timing Belt.
The Timing belt connects the crankshaft of the car to the camshaft. It’s purpose is to ensure that the valves open and close in sequence with the pistons. Not all vehicles have a timing belt.
The following is a more complete list of signs of a failing electrical system
- Vehicle won’t start with clicking sound
- Vehicle won’t start with no sound
- There is a grinding noise while cranking the engine
- Visual inspection or test light reveals blown fuse
- Vehicle starts but headlights dim while idling or at low speeds
- Alternator belt is found loose upon inspection
- Corrosion is present on wiring or on any part of the system
- Corrosion is present on battery terminals and/or cables
- Smell of burning plastic or electrical insulation
- Check engine light is illuminated
- Charging system warning light is illuminated
- Air conditioning isn’t working (due to compressor belt failure)
- Engine is overheating (due to water pump belt failure)
- Noisy idler pulley – whining/whirring or screeching noise
- Loud slapping, squealing or knocking noises coming from under the hood
- Battery test reveals failed battery
- Blown fuse discovered with test light or upon inspection
How To Jump Start A Dead Battery
If your battery isn’t charged enough to get your engine started then your two options to avoid having it towed to the shop are an overnight charger or jump starting it. Jump starting the battery is quite common since vehicle owners keep jumper cables handy and if you don’t have a set, then your neighbor might. Here is how to jump start a vehicle:
Park a working vehicle in a position where the jumper cables can reach from your battery to theirs. Both vehicles should be in park. The working vehicle is turned off.
- Attach the red cable to the positive terminal of the dead battery.
- Attach the other end of the red cable to the positive terminal of the live battery.
- (avoid letting loose cable ends touch each other, avoid letting the red cable touch the negative terminals, or the black cable touching the positive terminals)
- Attach the black cable to the negative terminal of the live battery.
- Attach the other end of the black cable to negative terminal of the dead battery or to a non-painted metal.
- Turn on the working engine and let it run for a couple minutes.
- Start your vehicle, if it won’t start let the other vehicle keep running a little longer then try again, you can also try revving the working vehicle.
- Disconnect the black cable from the jumped negative terminal
- Disconnect the black cable from the donor negative terminal
- Disconnect the red cable from the donor positive terminal
- Disconnect the red cable from the jumped positive terminal
Now that your vehicle is started you can drive it to the shop where we can fix it.
Hybrid Electrical System
A hybrid electrical system is a little more advanced than regular gasoline engines. The battery is used to partially power the drive of the vehicle and it has a special recharging system that includes the brakes.
Learn more about Hybrid Auto Repair.
Electrical System Repair
The most common electrical system repair is a battery replacement. The next most common is replacing a blown fuse. Other repairs might include replacing or reconnecting a shorted wire, or other faulty part of the electrical system. See also Chassis Electrical System Repair. Any starter system repairs, ignition system repairs, or charging system repairs would be considered electrical system repairs.
Charging System Repair, Alternator Repair
If the alternator is failing to recharge the battery then the issue is either with the alternator belt or the alternator itself. If the alternator belt is a serpentine belt then there will be other signs with the air conditioning and cooling system. The belt may need to be replaced or there could be an oil leak which is affecting the belt, or there could be a problem with the belt tensioner, which is supposed to prevent a good belt from loosening. Best case scenario out of these possibilities is that the vehicle just needs an alternator belt replacement. Yet, if it’s a serpentine belt then the labor can be intense depending on how long the belt is and how many pulleys are involved.
If the problem is with the alternator itself then the two options are an alternator rebuild or an alternator replacement. An alternator rebuild is generally less expensive.
Starter System Repair
If the vehicle won’t start it could be any number of problems, only some of which are related to the starter system. It will be the technician’s job to identify why the vehicle won’t start, but it could also be the air intake system. Starter system repair might include solenoid replacement or starter motor replacement.
Ignition System Repair
Engine misfiring is a common indicator for ignition system repair. The engine Tune-Up is a common maintenance service that could also be considered an ignition system repair service, since the spark plugs are replaced, among other adjustments to optimize the firing order. The ignition system is closely related to the exhaust and emissions system which are all monitored together.
The following is a more complete list of electrical system repairs:
- Alternator belt replacement
- Battery cable replacement
- Battery replacement
- Battery cable service
- Serpentine belt replacement (AC belt replacement, water pump belt replacement)
- Drive belt tensioner repair
- Drive belt replacement
- Timing belt replacement
- Serpentine belt pulley repair
- Serpentine tensioner repair
- Starter repair
- Ignition switch replacement
- Starter motor replacement
- Solenoid replacement
- Ballast resistor replacement
- Distributor cap and rotor replacement
- Ignition pickup replacement
- Ignition cable replacement (spark plug wire replacement)
- Ignition coil replacement
- Ignition igniter replacement
- Ignition relay replacement
- Spark plug replacement
- Tune up
- Camshaft position sensor replacement
- Crankshaft position sensor replacement
- Instrument voltage regulator replacement
Call 480-201-0740 For Electrical System Repairs
If your vehicle isn’t starting or if you have other electrical issues then bring it to Crawford’s Auto Repair today. We don’t pay staff by commissions and we never try to sell unnecessary repairs. Our highly trained technicians will treat your vehicle as if it belonged to our own mother and give you a straightforward presentation of the findings. Call 480-201-0740 to schedule an appointment today.


No Comments
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.